
A whole-home backup generator is no longer a luxury; nowadays, it is a necessity, as reliable power is becoming increasingly important. A whole-home generator, unlike a portable unit, automatically kicks in during a power outage, keeping your lights on, your food cold, and your life going. However, it is not as easy as selecting a model off the shelf to get the right one.
The most important thing that you do is to size your generator. A unit that is too small will not be able to run your essential appliances, resulting in overloads and possible damage. AA’s huge one is a waste of money in terms of initial acquisition costs and fuel usage.
This guide will step you through the calculation of your power requirements, the understanding of essential sizing terms, and provide an example of a home of various types to help you make a wise choice.
Why Generator Size Matters
The appropriate size for your whole-home backup generator is a trade-off among size, efficiency, and price. Make a wrong call, and you may encounter vexing performance problems or unwarranted costs.
Efficiency and Performance
The primary role of a backup generator is to ensure a smooth power supply. If your generator is not large enough, it will fail to meet the high electrical load of turning on large appliances, such as an air conditioner or a well pump. This may cause breakers to trip in the system or even a total failure when you need it most. On the other hand, a large generator is more expensive to purchase and install, and it consumes more fuel than necessary. Therefore, energy is wasted, a nd the cost of operation increases.
Comfort and Safety
When power is cut off, you use your generator to power up essential systems. The right size of the unit will ensure that your HVAC system maintains a comfortable temperature, your refrigerator and freezer do not spoil your food, your lights stay on, and your internet remains connected. This is not only convenience but also safety, and the need to feel normalcy amid a stressful situation.
Long-Term Cost Savings
The correct sizing of a generator is worth it in the long run. A unit that operates at its optimal load is more economical and incurs less wear and tear. This translates to lower fuel costs and fewer maintenance requirements, thereby saving you money over the generator’s lifetime.
Power Ratings (Watts, kW, kWh): This is the amount of power needed to operate each device.<|human|>Knowledge of Power Ratings (Watts, kW, kWh): This is the power required to run each device.
The language of electrical power is essential for selecting the right generator size. The most fundamental measurements are the watts, kilowatts (kW), and kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Running Watts & Starting Watts.
There are two types of power needed by appliances. Running watts or rated watts are the amount of power that an appliance requires to run continuously. Starting watts (or surge watts) is the additional power needed during a short period when the motor or compressor of the appliance begins. Fridges, air conditioners, and sump pumps are appliances with a high starting wattage. A generator is required to provide this initial surge.
Kilowatts (kW) -The Core Measurement.
A kilowatt (kW) is simply 1,000 watts. The generator capacity is usually measured in kW. Whole-house backup systems are typically 10 kW in small homes and above 26 kW in large houses with high power needs.
.
kWh = Energy Stored or Used
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of measurement of energy consumption. Although it is more often associated with battery storage, it helps determine the duration of a generator’s power supply, depending on the fuel source and rate of consumption.
Calculating the Power Requirement of Your Home.
The best way to find the right size is to calculate your home’s electrical power requirement. Follow these four steps.
Step 1 -Enlist Critical and Non-Critical Loads.
Write down the names of all the appliances and systems that you would like to use when there is an outage. Separate them into necessities (such as the refrigerator, light, sump pump) and optionals (such as the oven or a second TV).
Step 2 -Check Appliance Wattages.
Determine the running and starting wattage for each item on your list. This is generally located on the appliance’s compliance plate or in the owner’s manual. The following presents the everyday essentials.
| Appliance | Running Watts | Starting Watts |
| Refrigerator | 700 | 2200 |
| Central AC (3 Ton) | 3500 | 7200 |
| Sump Pump | 800 | 1300 |
| Lights (10) | 180 (18W each) | – |
Step 3 – Add Up the Numbers
To determine the total power you require, add the running watts of all the appliances you intend to use simultaneously. Next, choose the highest starting wattage of any of your necessary appliances, then add it to your running total in watts.
Equation: The sum of the running watts and the highest starting watts = the total wattage required.
Step 4 – Add a 20% Safety Margin
It is prudent to put in a 20 percent buffer to your total calculation. This reserve will ensure that the generator does not operate at full capacity, which will ease the load and leave the potential for additional appliances in the future.
Suggested Generator sizing based on home type.
Although it is best to calculate the load in detail, you can use the size of your home as a starting point to make an estimate.
- Small Homes (1 -2 Bedrooms / Simple Loads)
Small homes could use a 7 kW-10 kW generator. This size accommodates necessities such as lights, a refrigerator, a small window air conditioner, and a few electronics.
- Medium Homes (3-4 Bedrooms /Normal loads)
For most medium-sized houses, a 12 kW to 20 kW generator can reliably power most appliances, such as a central HVAC unit, a well pump, and kitchen necessities.
- Big Houses (5 Bedrooms + / Loads High-Demand)
Big houses with more than one HVAC system, pool, or other high-demand loads will likely require a 22 kW-30 kW+ generator to maintain full-house comfort without performance loss.
Smart Tip
A licensed electrician should perform a professional load calculation to size a generator. This is the most accurate way to determine the generator’s size. They will examine the special electrical panel and power requirements of your home to make a specific recommendation.
Type of fuel and Run Time.
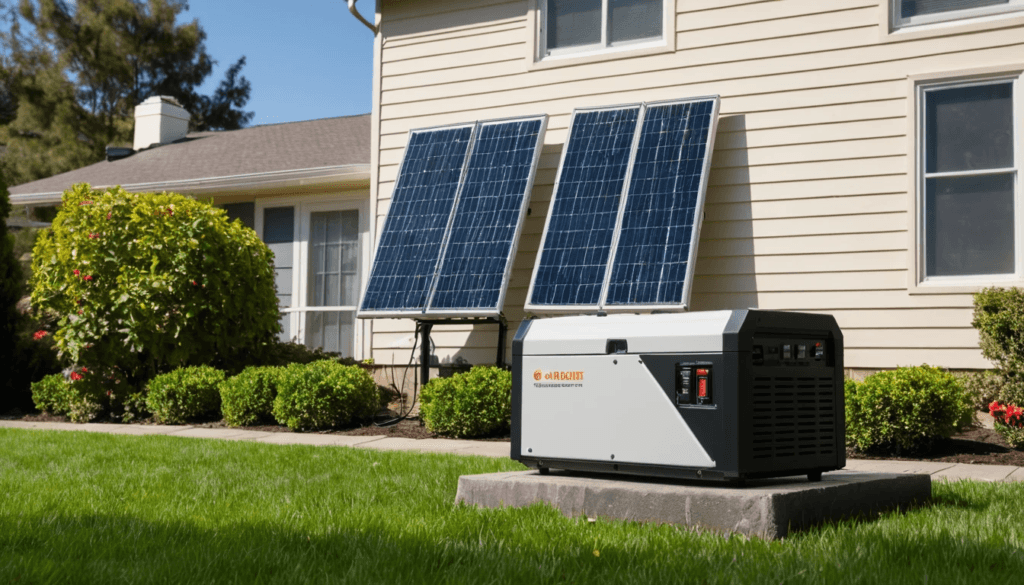
The fuel you feed your generator influences its maintenance, convenience, and the time it runs.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is connected to your utility line, and this means it is a virtually unlimited fuel source. It is a clean and convenient alternative for homeowners where the natural gas service is available.
Propane
Another clean and trustworthy alternative is liquid propane. It is kept in a large tank on your ground, and hence the size of the tank limits how long it can be run. It is a good option in rural regions where there is no natural gas.
Diesel
Diesel generators have a reputation for durability and extended engine life. But they are usually noisier, emit more, and require close fuel storage to avoid contamination.
Hybrid / Solar + Battery Assist
To the environmentally conscious, a combination of a generator, a solar panel, and a battery storage system can form a very efficient hybrid. As a last resort, the generator can be used once the solar and battery power are exhausted.
Installation Factors and Safety Factors.
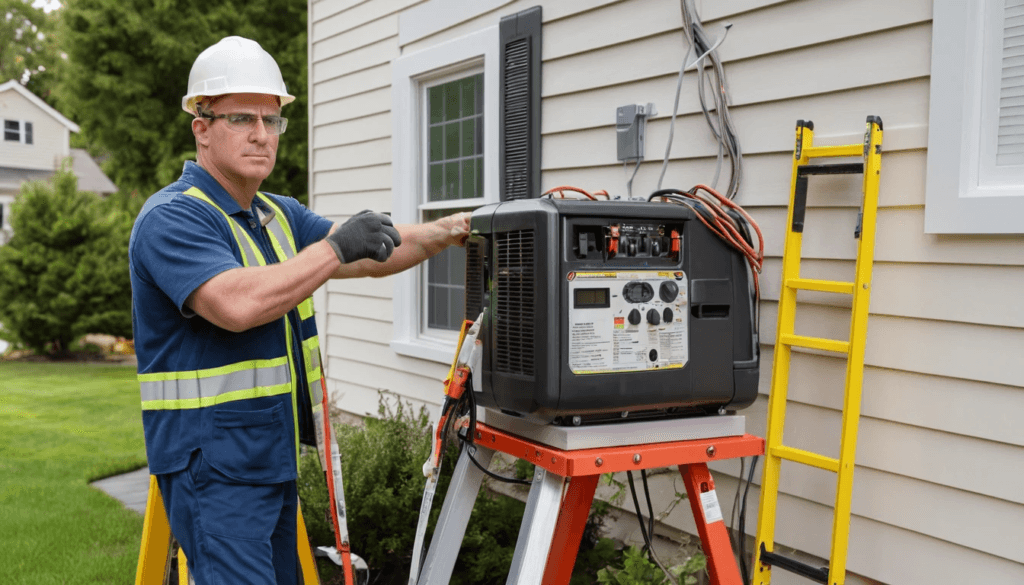

The safe and successful functioning of an entire-home generator cannot be discussed without proper installation.
Home Panel Connection Transfer Switch.
A transfer switch is an essential safety device that will separate your home from the utility grid when the generator is operating. This will avoid hazardous back-feeding, which may harm utility workers and destroy the grid.
Ventilation & Location
Generators emit carbon monoxide and should be placed outside on a flat surface, at a distance from windows, doors, and vents to ensure good ventilation.
Installation Permits and Professional.
Never ignore the local building codes and obtain the permits. It is always good to employ a certified installer to ensure your generator is installed correctly and safely.
Example Sizing Scenarios
The following are typical situations for demonstrating generator sizing.
- Scenario 1-2,000 sq ft Home (U.S average)
An average house of this size, equipped with a standard set of appliances and a central air conditioner, will need a 1518 kW system to run the necessities and ensure comfort in the event of a power outage.
- Scenario 2 -Off-Grid Cabin / Minimalist.
A 5-8 kW generator can power lights, a small refrigerator, and a water pump in a small cabin with efficient appliances and low power requirements.
- Scenario 3- Large House having 2 HVACs.
A huge house with two central air conditioners has a considerable power requirement. It would be advisable to have a 2530 kW generator to accommodate the surge loads of the two units starting.
Choose the correct option for your house.
The most crucial step towards striking a balance among reliability, efficiency, and cost is selecting the correct size for your whole-home backup generator. Knowing your power requirements and what determines performance, you can invest in a system that gives you the peace of mind in the years to come. It is always advisable to consult a professional to analyze the load before a final decision is made.
Are you willing to investigate your choices? See myelectricgenerators.com to get all sizing charts and our professional reviews of generators.


