
A sudden power outage can spoil food or ruin a camping trip. While traditional generators are noisy and run on gasoline, solar power stations are quieter and cleaner, offering an eco-friendly way to power your home, RV, or campsite.
This guide first explains solar generators and how to calculate their capabilities. You’ll learn the power needs of everyday appliances and RVs, helping you choose the right generator and confidently invest in reliable off-grid energy.
Let’s begin by understanding what a solar generator is and how it differs from other options.
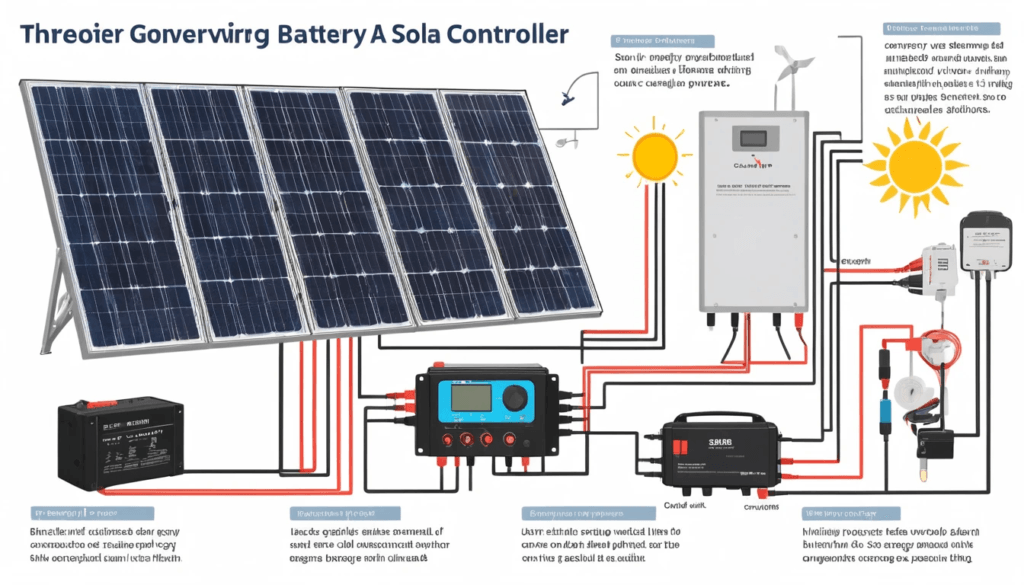
Solar generators are large, portable battery packs charged by solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity. They offer quiet, low-maintenance alternatives to gas-powered generators, which use fossil fuels and emit noise and exhaust.
Their popularity comes from use as backup home power, RV power, and electricity for remote camps. Main advantages include clean energy, portability, and freedom from fossil fuels.
With this foundation in place, let’s explore how solar generators actually deliver power to your appliances.
To understand a solar generator’s potential, distinguish it from a standard generator. A standard generator burns fuel to produce electricity, whereas a solar generator relies on solar panels to generate and store electricity in its battery. Recognising these differences helps explain what determines each system’s performance.
Gas generators create electricity by burning fuel, which is then used directly or to charge batteries. In contrast, solar generators convert sunlight into electricity through solar panels, storing it in a battery without burning fuel or producing emissions. The stored electricity can safely power household appliances.
Next, let’s examine the significant factors that affect how long your solar generator can run.
A solar generator is a device that is characterised by three major elements:
- Battery: The generator’s core. Watt-hours (Wh) show how much energy the battery stores. A larger battery (higher Wh) means more power for more extended device use.
- Inverter: Its watt (W) rating shows the maximum power it delivers at any time. It converts battery DC to AC for household appliances.
- Controller: Manages energy flow between solar panels and the battery, prevents overcharging, and keeps charging efficient to support battery health.
To understand these elements further, let’s break down standard power terms and calculations.
Think of it like this:
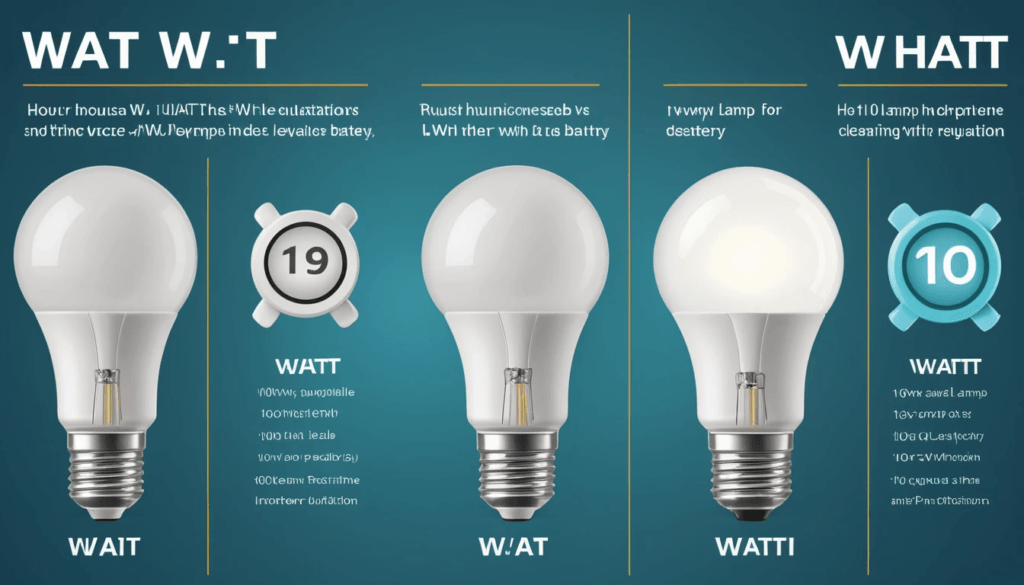
Wattage (W): Wattage is a measure of how much electrical power a device uses at any moment. For example, a 100-watt (W) lamp will use power ten times as fast as a 10-watt lamp.
Watt-hours (Wh): This term describes the total amount of energy stored or used over time, like the amount of gas in a car’s tank. For example, a 1000Wh battery can deliver 1000 watts for one hour or 100 watts for 10 hours.
To find out how long a generator can power something, divide the battery’s watt-hours by the device’s wattage. For example, a 500Wh battery powering a 100W TV would last 5 hours (500Wh ÷ 100W = 5 hours).
Now that you understand the key terms, let’s estimate how much power appliances like fridges and RVs actually use.
How much power your appliances use is something you need to know before you can determine how long a generator will last.
Average power consumption of domestic and RV refrigerators.
Fridges do not run constantly; they cycle on and off, using less energy. Several factors affect how much power a refrigerator uses:
- Size and Age: Larger, older fridges are less efficient.
- Insulation: Poor insulation makes the compressor work harder.
- Ambient Temperature: A fridge in a hot garage uses more energy than one in a fabulous kitchen.
- Each door opening lets cold air escape, requiring the compressor to cool again.
With an understanding of your appliance’s power use, the next step is to calculate how much battery capacity you need to keep them running.
Check the appliance label for wattage. If it only lists amps (A) and volts (V), multiply them to get watts (W = V × A). To find daily energy use, multiply the running wattage by the hours used per day. For example, 150 watts for 8 hours equals 1200 watt-hours per day.
An example is a fridge with a 150W consumption for 8 hours a day: 150W × 8 hours = 1200 Wh/day.
Let’s apply these calculations to find out exactly how long a solar generator can keep a fridge running.
The generator’s size determines how long it can run a fridge. For 150W over 8 hours: 150W × 8 hours = 1200 Wh/day.
1000Wh Generator: It can power most energy-efficient fridges in the house for 8-12 hours, enough to get through an overnight power outage.
A 2000Wh+ generator powers an average fridge for a day or more. With sunlight, you can recharge the generator. Solar panels can power a refrigerator and recharge a 1000-2000Wh battery to full, letting the system run indefinitely when conditions allow.
Solar generators also play a crucial role when powering RVs. Here’s how their duration changes in this context.
Powering an RV is more complex because of the multiple systems involved.
Typical RV Power Demands
RV power use can add up quickly. An RV uses 1000-3000Wh daily; large RVs with AC may use 5000Wh or more.
- Electronics (TV, chargers): 40-60W.
- Water Pump: 50-100W.
Optimising how you use power in your RV will directly affect your solar generator’s runtime. Here’s how you can maximise your energy resources.
Managing RV power use extends the runtime of solar generators. Reduce the use of high-drain devices, such as air conditioners. With a 2000Wh generator and 400W solar panels, you can power essentials like a fridge, lights, and a pump off-grid, as long as you avoid heavy appliances.
The Energy-Saving Tip: Switch appliances off when you do not use them, replace existing lights with energy-efficient ones, and ensure your fridge is complete (a full fridge retains the cold longer).
Add panels for faster charging or expand battery capacity. For battery health, avoid fully discharging it; most makers recommend keeping the charge between 20% and 80%. Store the generator charged at 20-80% for best long-term health. Use 500-1000Wh for camping or short outages; 2000-4000Wh models suit RVs or home backup.
Safety and Warranty: Choose brands with a strong track record, strong warranties, and safety certifications such as UL.
A 1000-1500Wh generator can usually keep an efficient fridge running overnight.
- But what happens when your solar generator’s battery runs out? Understanding this scenario is essential for planning.
When the battery depletes, all connected appliances lose power. Recharge the generator with an outlet or solar panel before reusing. Charging time depends on usage and panel wattage. Allow at least 4-6 hours of peak sunlight. Cloudy days slow charging substantially.
To conclude, what key lessons can you apply from this discussion? Let’s summarise how solar generators fit into off-grid living.
A solar generator helps you achieve energy independence if you match its output to your needs. Start small and expand as you learn. This approach builds a custom power system for your needs and budget.

